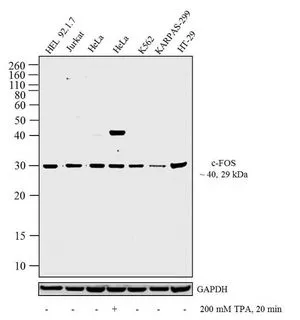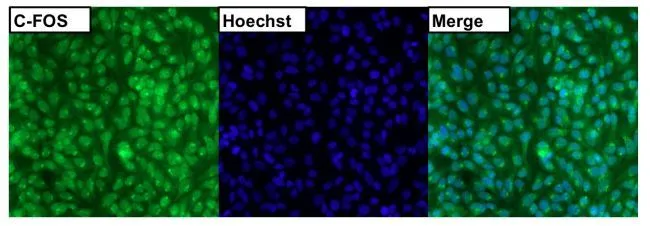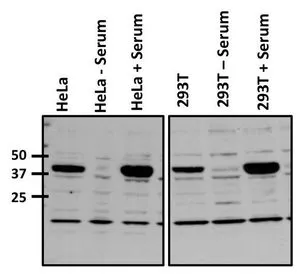
GTX25794 WB Image
c-Fos antibody - Orthogonal Validated

GTX25794
ApplicationsFlow Cytometry, ImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman, Mouse
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product Namec-Fos antibody - Orthogonal Validated
- Delivery Days Customer10
- ApplicationsFlow Cytometry, ImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Scientific DescriptionCellular oncogenes, or proto-oncogenes, play pivotal roles in cellular communication pathways that regulate normal growth, development and differentiation. The cellular oncogene families fos and jun encode nuclear proteins that can function as transcription factors. The fos family of nuclear oncogenes encode cFos, FosB, (fos-related antigen) Fra1, and Fra2. Fos and Jun dimerize to form Activator Protein-1 (AP-1), a transcriptional factor that binds to the 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol 13-acetate (TPA) response element (TRE) of several cellular and viral genes including human collagenase, metallothionein IIa, stromelysin, interleukin 2, SV40 and polyoma. Fos and Jun contain the leucine-zipper motif that allows for dimerization and an adjacent basic domain required for biological activity. The functionally active form of Fos is in a heterodimer with a member of the Jun family. While Jun family members can form functional homodimers, studies indicate that Fos family members do not self-associate and therefore do not bind DNA on their own. The various dimers differ in their ability to transactivate AP-1 dependent genes.
- ReactivityHuman, Mouse
- Storage Instruction2°C to 8°C,-20°C
- UNSPSC12352203
References
- Molecular mechanisms underlying altered neurobehavioural development of female offspring of mothers with polycystic ovary syndrome: FOS-mediated regulation of neurotrophins in placenta. Wang F et al., 2020 Oct, EBioMedicineRead more
- Molecular mechanisms underlying altered neurobehavioural development of female offspring of mothers with polycystic ovary syndrome: FOS-mediated regulation of neurotrophins in placenta. Wang F et al., 2020 Oct, EBioMedicineRead more