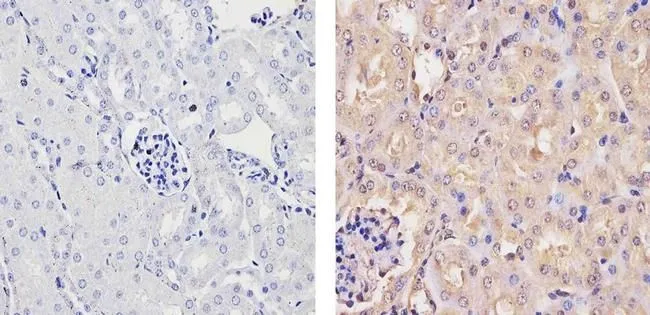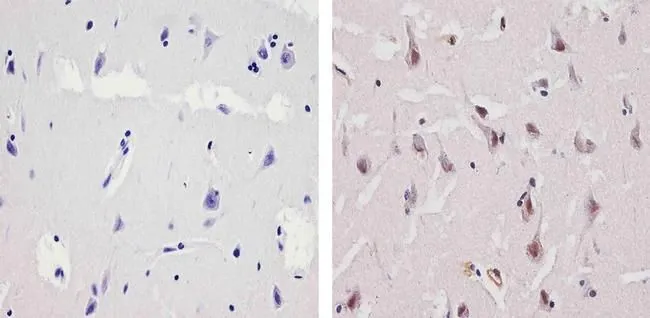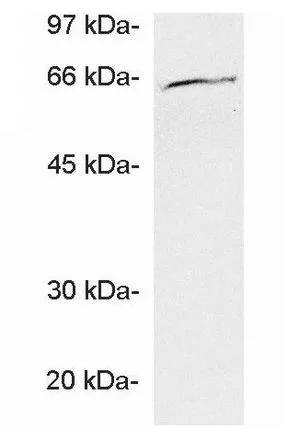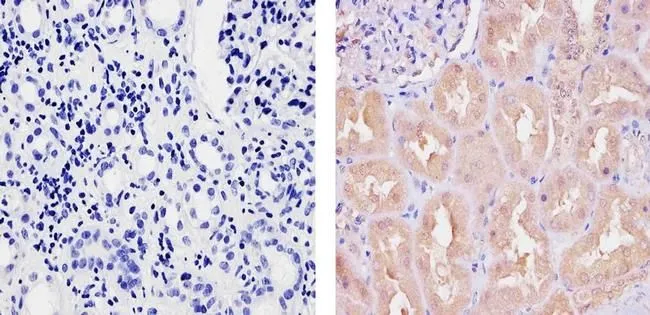
GTX23341 IHC-P Image
Ubiquilin 1 antibody

GTX23341
ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHamster, Human, Mouse
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameUbiquilin 1 antibody
- Delivery Days Customer10
- ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- Concentration1 mg/ml
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Scientific DescriptionAmyloid beta peptide is the major constituent of amyloid plaques in the brains of individuals afflicted with Alzheimers disease. This peptide is generated from the beta-amyloid precursor protein (beta APP) in a two-step process. The first step involves cleavage of the extracellular, amino-terminal domain of beta APP. Protein cleavage is performed by an aspartyl protease termed beta-secretase (BACE). This enzyme is synthesized as a propeptide that must be modified to the mature and active form by the prohormone convertase, furin. Beta APP cleavage by the mature form of BACE results in the cellular secretion of a segment of beta APP and a membrane-bound remnant. This remnant is then processed by another protease termed gamma-secretase. Gamma-secretase cleaves an intra-membrane site in the carboxyl-terminal domain of beta APP, thus generating the amyloid beta peptide. Gamma-secretase is believed to be a multi-subunit complex containing presenilin-1 and 2 as central components. Found associated with the presenilins are nicastrin and ubiquilin. Nicastrin has been found to bind to the carboxyl-terminus of beta APP and helps to modulate the production of the amyloid beta peptide. Ubiquilin is believed to promote presenilin protein accumulation. Also found in the neurofibrillary lesions associated with Alzheimers disease is a protein termed Tau. Tau is a neuronal microtubule-associated protein found predominantly on axons. Tau functions to promote tubulin polymerization and stabilize microtubules. Tau, in its hyperphosphorylated form, is the major constituent of paired helical filaments (PHF), which are the building block of neurofibrillary lesions found in brain tissue of Alzheimers diseased patients.
- ReactivityHamster, Human, Mouse
- Storage Instruction2°C to 8°C,-20°C
- UNSPSC12352203