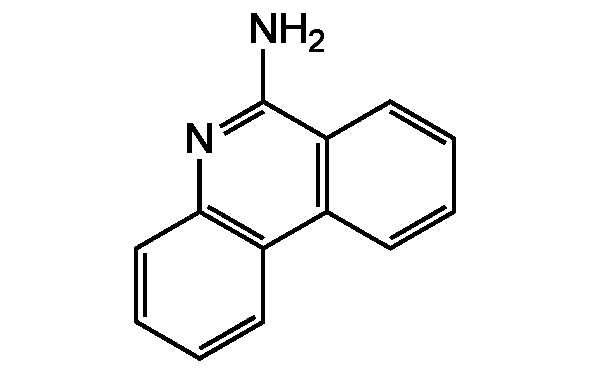
Chemical Structure
6-Aminophenanthridine [832-68-8]

AG-MR-C0029
Estimated Purity>97% (HPLC)
Product group Chemicals
Molecular Weight194.2
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product Name6-Aminophenanthridine [832-68-8]
- Delivery Days Customer10
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>97% (HPLC)
- Hazard InformationNon-hazardous,Warning
- Molecular FormulaC13H10N2
- Molecular Weight194.2
- Scientific DescriptionAntiprion agent. Ribosome-borne protein folding activity (RPFA) inhibitor. Binds to the ribosomal RNA and inhibits specifically the protein folding activity of the ribosome. Inhibitor of protein aggregation. - Chemical. CAS: 832-68-8. Formula: C13H10N2. MW: 194.2. Antiprion agent. Ribosome-borne protein folding activity (RPFA) inhibitor. Binds to the ribosomal RNA and inhibits specifically the protein folding activity of the ribosome. Inhibitor of protein aggregation.
- SMILESNC1=NC2=C(C=CC=C2)C2=C1C=CC=C2
- Storage Instruction2°C to 8°C,-20°C
- UNSPSC12352200
References
- An expeditious synthesis of 6-aminophenanthridines: F. Gug, et al.; THL 46, 3725 (2005)
- Protein folding activity of ribosomal RNA is a selective target of two unrelated antiprion drugs: D. Tribouillard-Tanvier, et al.; PLoS One 3, e2174 (2008)
- Tools for the study of ribosome-borne protein folding activity: C. Voisset, et al.; Biotechnol. J. 3, 1033 (2008)
- Mode of action of the antiprion drugs 6AP and GA on ribosome assisted protein folding: S.D. Reis, et al.; Biochimie 93, 1047 (2011)
- Antiprion drugs 6-aminophenanthridine and guanabenz reduce PABPN1 toxicity and aggregation in oculopharyngeal muscular dystrophy: N. Barbezier, et al.; EMBO Mol. Med. 3, 35 (2011)
- The antiprion compound 6-aminophenanthridine inhibits the protein folding activity of the ribosome by direct competition: Y. Pang, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 288, 19081 (2013)
