Chemical Structure
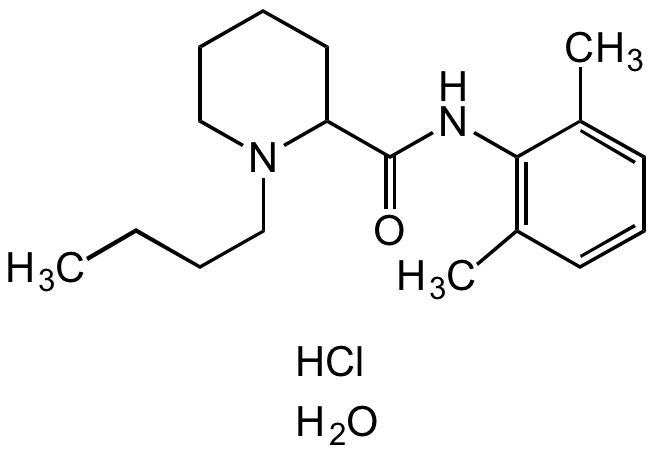
Bupivacaine hydrochloride monohydrate [73360-54-0]

CDX-B0326
CAS Number73360-54-0
Product group Chemicals
Estimated Purity>98%
Molecular Weight288.4. 36.5 . 18.0
Overview
- SupplierChemodex
- Product NameBupivacaine hydrochloride monohydrate [73360-54-0]
- Delivery Days Customer10
- ADR Class6.1
- CAS Number73360-54-0
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>98%
- Hazard InformationDanger,Excepted quantity
- Molecular FormulaC18H28N2O . HCl . H2O
- Molecular Weight288.4. 36.5 . 18.0
- Scientific DescriptionBupivacaine is an amino amide local anesthetic that decreases current amplitude and inhibits whole cell K+ currents in Ca2+-activated K+ channels and N-type voltage-gated (KCNA and KCNC) K+ channels. Bupivacaine also inhibits voltage-gated Na+ channels and tandem pore domain (TASK-2/KCNK-5) K+ channels. The compound is cytotoxic at high concentrations inducing apoptosis and/or necrosis by interference with the mitochondrial energy transduction. Shown to inhibit aerobic ATP synthesis by (i) uncoupling of the oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS) and (ii) inhibition of the complex I of the respiratory. Other mechanisms include inhibition of the carnitine-acylcarnitine translocase or activation of the mitochondrial permeability transition pore (MPTP). The analgesic effects of bupivicaine are thought to potentially be due to its binding to the prostaglandin E2 receptors, subtype EP1 (PGE2EP1), which inhibits the production of prostaglandins, thereby reducing fever, inflammation, and hyperalgesia. It is employed as cAMP production inhibitor, it acts as a surfactant molecule possessing both hydrophilic and lipophilic properties, adrenergic antagonist and cholinesterase inhibitor. - Chemical. CAS: 73360-54-0. Formula: C18H28N2O . HCl . H2O. MW: 288.4. 36.5 . 18.0. Synthetic. Bupivacaine is an amino amide local anesthetic that decreases current amplitude and inhibits whole cell K+ currents in Ca2+-activated K+ channels and N-type voltage-gated (KCNA and KCNC) K+ channels. Bupivacaine also inhibits voltage-gated Na+ channels and tandem pore domain (TASK-2/KCNK-5) K+ channels. The compound is cytotoxic at high concentrations inducing apoptosis and/or necrosis by interference with the mitochondrial energy transduction. Shown to inhibit aerobic ATP synthesis by (i) uncoupling of the oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS) and (ii) inhibition of the complex I of the respiratory. Other mechanisms include inhibition of the carnitine-acylcarnitine translocase or activation of the mitochondrial permeability transition pore (MPTP). The analgesic effects of bupivicaine are thought to potentially be due to its binding to the prostaglandin E2 receptors, subtype EP1 (PGE2EP1), which inhibits the production of prostaglandins, thereby reducing fever, inflammation, and hyperalgesia. It is employed as cAMP production inhibitor, it acts as a surfactant molecule possessing both hydrophilic and lipophilic properties, adrenergic antagonist and cholinesterase inhibitor.
- SMILESCCCCN1CCCCC1C(NC2=C(C)C=CC=C2C)=O.Cl.O
- Storage InstructionRT
- UN Number2811
- UNSPSC12352200
