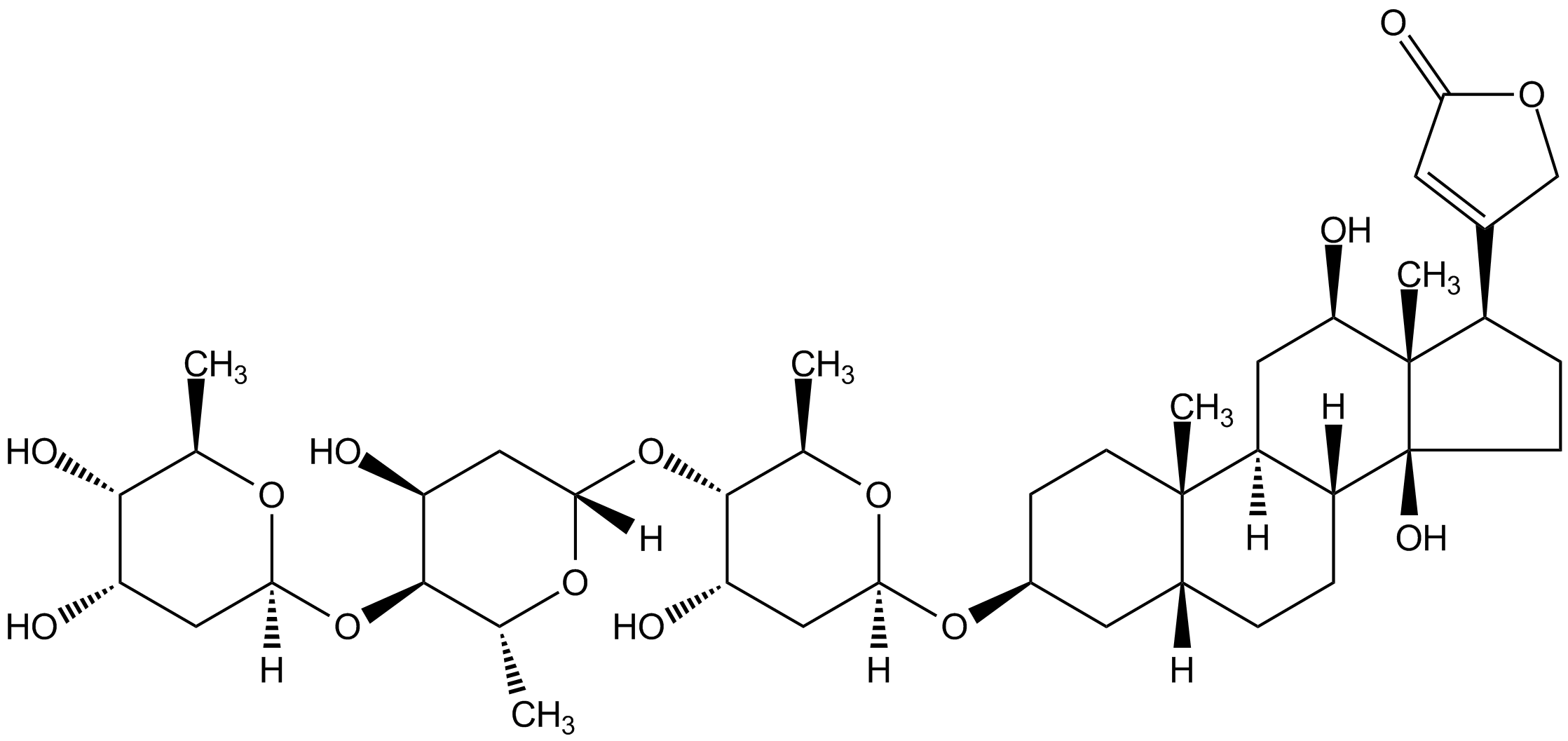
Chemical Structure
Digoxin [20830-75-5]

CDX-D0175
CAS Number20830-75-5
Product group Chemicals
Estimated Purity>95%
Molecular Weight780.94
Overview
- SupplierChemodex
- Product NameDigoxin [20830-75-5]
- Delivery Days Customer10
- ADR Class6.1
- CAS Number20830-75-5
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>95%
- Hazard InformationDanger,Excepted quantity
- Molecular FormulaC41H64O14
- Molecular Weight780.94
- Scientific DescriptionCardiac glycoside from the leaves of Digitalis lanata. It is used to treat cardiac arrhythmias. It is often used as a model substrate of P-glycoprotein (Pgp) (0.01-10microM) and an inhibitor of Na+/K+-ATPase. Inhibits membrane-bound alpha-subunits of the Na+/K+ ATPase pump in myocytes. The primary mechanism of action involves inhibition of the Na+/K+ ATPase, mainly in the myocardium. This inhibition causes an increase in intracellular sodium levels, resulting in a reversal of the action of the sodium-calcium exchanger, which causes an increase in the intracellular calcium concentration. This leads to a decrease in heart rate and increased storage of calcium in the sarcoplasmic reticulum, causing a corresponding increase in the release of calcium during each action potential. - Chemical. CAS: 20830-75-5. Formula: C41H64O14. MW: 780.94. Synthetic. Cardiac glycoside from the leaves of Digitalis lanata. It is used to treat cardiac arrhythmias. It is often used as a model substrate of P-glycoprotein (Pgp) (0.01-10microM) and an inhibitor of Na+/K+-ATPase. Inhibits membrane-bound alpha-subunits of the Na+/K+ ATPase pump in myocytes. The primary mechanism of action involves inhibition of the Na+/K+ ATPase, mainly in the myocardium. This inhibition causes an increase in intracellular sodium levels, resulting in a reversal of the action of the sodium-calcium exchanger, which causes an increase in the intracellular calcium concentration. This leads to a decrease in heart rate and increased storage of calcium in the sarcoplasmic reticulum, causing a corresponding increase in the release of calcium during each action potential.
- SMILES[H][C@@]1(C[C@H](O)[C@H](O[C@@]2([H])C[C@H](O)[C@H](O[C@@]3([H])C[C@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](C)O3)[C@@H](C)O2)[C@@H](C)O1)O[C@H]1CC[C@@]2(C)[C@]([H])(CC[C@]3([H])[C@]2([H])C[C@@H](O)[C@]2(C)[C@H](CC[C@]32O)C2=CC(=O)OC2)C1
- Storage Instruction2°C to 8°C,-20°C
- UN NumberUN 3462
- UNSPSC12352200
