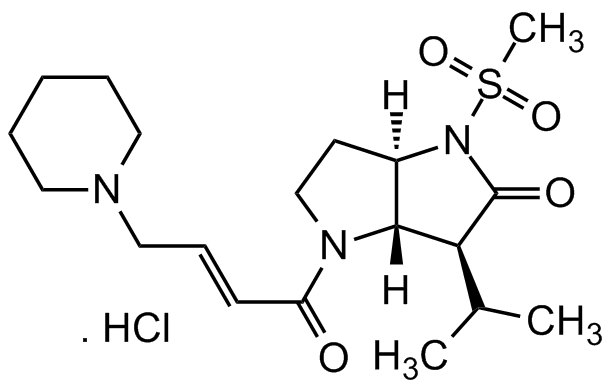
Chemical Structure
GW311616A [197890-44-1, 198062-54-3]

AG-CR1-3632
Estimated Purity>98% (NMR)
Product group Chemicals
Molecular Weight397.5 . 36.5
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product NameGW311616A [197890-44-1, 198062-54-3]
- Delivery Days Customer10
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>98% (NMR)
- Hazard InformationNon-hazardous,Warning
- Molecular FormulaC19H31N3O4S . HCl
- Molecular Weight397.5 . 36.5
- Scientific DescriptionChemical. CAS: 197890-44-1. Formula: C19H31N3O4S . HCl. MW: 397.5 . 36.5. Potent, selective intracellular neutrophil elastase (NE, alpha-1-proteinase) inhibitor (by covalently binding to NE). Inhibits human neutrophil elastase (HNE) and is selective over other human serine proteases with IC50 values of 22nM for HNE, >100microM for trypsin, cathepsin G and plasmin, >3microM for chymotrypsin and tissue plasminogen activator. Specific beta-cell proliferation promoter. Similar to SerpinB1, which functions through its inhibiting activity of several proteases including neutrophil elastase, cathepsin G and proteinase-3. Reverses insulin resistance and body weight gain in HFD-fed mice, suggesting that the SerpinA1-NE system regulates AMPK signaling, fatty acid oxidation (FAO) and energy expenditure. The imbalance between SerpinA1 (alpha1-antitrypsin; A1AT) and neutrophil elastase NE contributes to the development of obesity and related inflammation, insulin resistance and liver steatosis. Shown to inhibit tumor cell growth and proliferation and induce apoptosis in leukemia cell lines. - Potent, selective intracellular neutrophil elastase (NE, alpha-1-proteinase) inhibitor (by covalently binding to NE). Inhibits human neutrophil elastase (HNE) and is selective over other human serine proteases with IC50 values of 22nM for HNE, >100microM for trypsin, cathepsin G and plasmin, >3microM for chymotrypsin and tissue plasminogen activator. Specific beta-cell proliferation promoter. Similar to SerpinB1, which functions through its inhibiting activity of several proteases including neutrophil elastase, cathepsin G and proteinase-3. Reverses insulin resistance and body weight gain in HFD-fed mice, suggesting that the SerpinA1-NE system regulates AMPK signaling, fatty acid oxidation (FAO) and energy expenditure. The imbalance between SerpinA1 (alpha1-antitrypsin; A1AT) and neutrophil elastase NE contributes to the development of obesity and related inflammation, insulin resistance and liver steatosis. Shown to inhibit tumor cell growth and proliferation and induce apoptosis in leukemia cell lines.
- SMILES[H]Cl.[H][C@@]1(CCN2C(/C=C/CN3CCCCC3)=O)[C@]2([H])[C@H](C(C)C)C(N1S(C)(=O)=O)=O
- Storage Instruction2°C to 8°C,-20°C
- UNSPSC12352200
References
- The discovery of a potent, intracellular, orally bioavailable, long duration inhibitor of human neutrophil elastase-GW311616A a development candidate: S.J. Macdonald, et al.; Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 11, 895 (2001)
- Imbalance between neutrophil elastase and its inhibitor alpha1-antitrypsin in obesity alters insulin sensitivity, inflammation, and energy expenditure: V. Mansuy-Aubert, et al.; Cell Metab. 17, 534 (2013)
- Neutrophil elastase and its therapeutic effect on leukemia cells: K.L. Jiang, et al.; Mol. Med. Rep. 12, 4165 (2015)
- SerpinB1 Promotes Pancreatic beta Cell Proliferation: A. El Ouaamari, et al.; Cell Metab. 23, 194 (2016)
