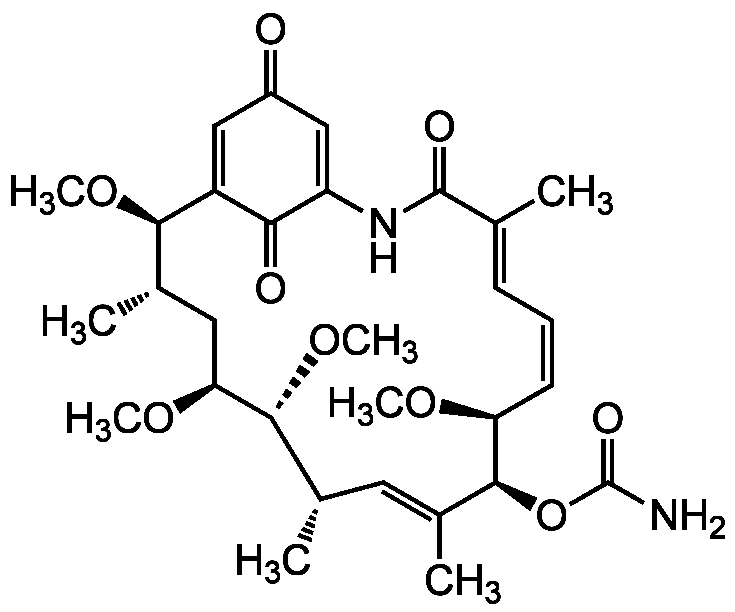
Chemical Structure
Herbimycin A [70563-58-5]

AG-CN2-0429
CAS Number70563-58-5
Product group Chemicals
Estimated Purity>99%
Molecular Weight574.7
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product NameHerbimycin A [70563-58-5]
- Delivery Days Customer10
- CAS Number70563-58-5
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>99%
- Hazard InformationNon-hazardous
- Molecular FormulaC30H42N2O9
- Molecular Weight574.7
- Scientific DescriptionBenzoquinone ansamycin antibiotic. Herbicidal compound. Potent, selective, irreversible and cell permeable protein tyrosine kinase inhibitor. Inhibitor of v-Src, Yes, Fps, Ros, Bcr-Abl and ErbB oncogene products. Antitumor compound. Antiangiogenic. Inhibits NF-kappaB activation and phosphorylation of phospholipase C-gamma1. Inhibitor of heat shock protein 90 (Hsp90). Binds Hsp90 and destabilizes client proteins leading to their ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation. Increases the sensitivity of certain cancer cells to chemotherapeutic agents. Neuroprotective. Antiparasitic, antischistosomal agent. Antiviral. Increase microtubules sensitivity to cold in plants. - Chemical. CAS: 70563-58-5. Formula: C30H42N2O9. MW: 574.7. Isolated from Streptomyces sp. Benzoquinone ansamycin antibiotic. Herbicidal compound. Potent, selective, irreversible and cell permeable protein tyrosine kinase inhibitor. Inhibitor of v-Src, Yes, Fps, Ros, Bcr-Abl and ErbB oncogene products. Antitumor compound. Antiangiogenic. Inhibits NF-kappaB activation and phosphorylation of phospholipase C-gamma1. Inhibitor of heat shock protein 90 (Hsp90). Binds Hsp90 and destabilizes client proteins leading to their ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation. Increases the sensitivity of certain cancer cells to chemotherapeutic agents. Neuroprotective. Antiparasitic, antischistosomal agent. Antiviral. Increase microtubules sensitivity to cold in plants.
- SMILESCO[C@H]1C[C@H](C)[C@@H](OC)C2=CC(=O)C=C(NC(=O)\C(C)=C\C=C/[C@H](OC)[C@@H](OC(N)=O)\C(C)=C\[C@H](C)[C@H]1OC)C2=O
- Storage Instruction2°C to 8°C,-20°C
- UNSPSC12352200
References
- Herbimycin, a new antibiotic produced by a strain of Streptomyces: S. Omura, et al.; J. Antibiot. (Tokyo) 32, 255 (1979)
- A new activity of herbimycin A: inhibition of angiogenesis: T. Yamashita, et al.; J. Antibiot. (Tokyo) 42, 1015 (1989)
- Effects of herbimycin A and various SH-reagents on p60v-src kinase activity in vitro: H. Fukazawa, et al; BBRC 173, 276 (1990)
- Use and selectivity of herbimycin A as inhibitor of protein-tyrosine kinases: Y. Uehara & H. Fukazawa; Methods Enzymol. 201, 370 (1991)
- Specific inhibition of cytoplasmic protein tyrosine kinases by herbimycin A in vitro: H. Fukazawa, et al.; Biochem. Pharmacol. 42, 1661 (1991)
- Induction of differentiation of human leukemia cells with a structurally altered c-abl (bcr/abl) gene by herbimycin A, an inhibitor of tyrosine kinase activity: Y. Honma, et al.; Leukemia 6, 229 (1992)
- Effect of herbimycin A, an inhibitor of tyrosine kinase, on protein tyrosine kinase activity and phosphotyrosyl proteins of Ph1-positive leukemia cells: M. Okabe, et al.; Leuk. Res. 18, 213 (1994)
- Evidence for direct modification of NF kappa B by the tyrosine kinase inhibitor, herbimycin A: T.M. Mahon & L.A. O'Neill; Biochem. Soc. Trans. 23, 111S (1995)
- Herbimycin A induces the 20 S proteasome- and ubiquitin-dependent degradation of receptor tyrosine kinases: L. Sepp-Lorenzino, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 270, 16580 (1995)
- Inhibition of PDGF-induced phospholipase D but not phospholipase C activation by herbimycin A: B.Y. Kim; BBRC 212, 1061 (1995)
