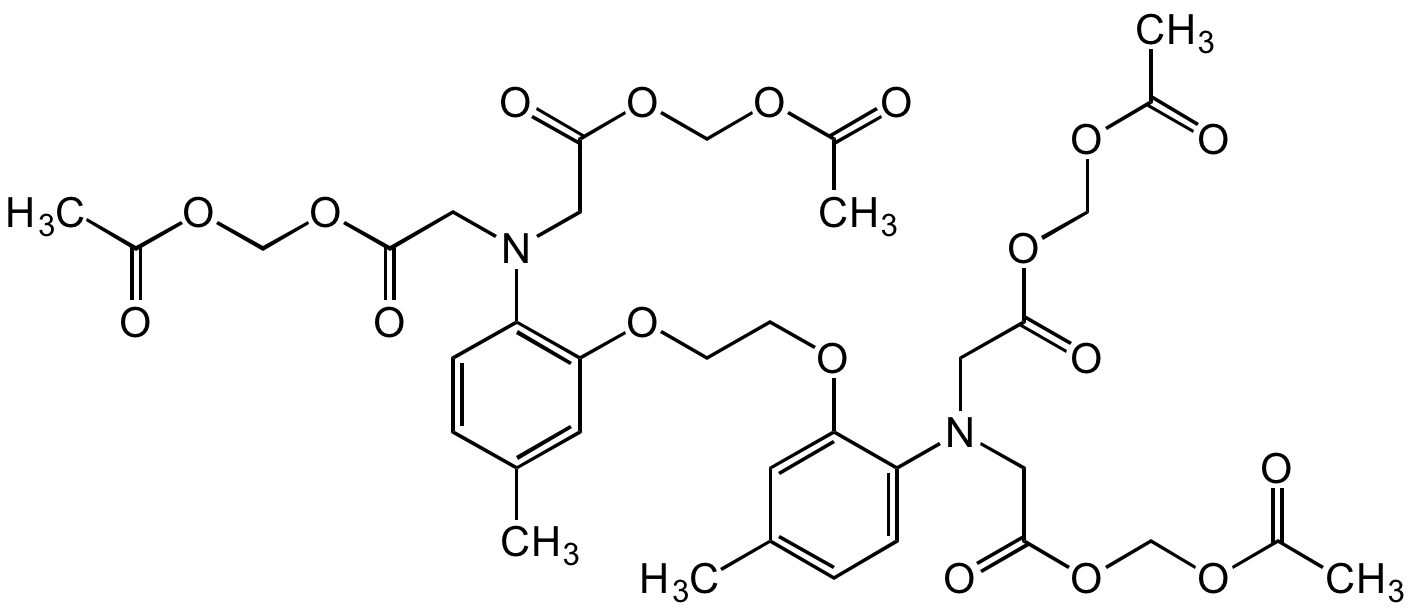
Chemical Structure
MAPTAM [147504-94-7]

CDX-B0292
CAS Number147504-94-7
Product group Chemicals
Estimated Purity>94%
Molecular Weight792.74
Overview
- SupplierChemodex
- Product NameMAPTAM [147504-94-7]
- Delivery Days Customer10
- CAS Number147504-94-7
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>94%
- Hazard InformationNon-hazardous,Warning
- Molecular FormulaC36H44N2O18
- Molecular Weight792.74
- Scientific DescriptionChemical. CAS: 147504-94-7. Formula: C36H44N2O18. MW: 792.74. Synthetic. MAPTAM is a cell permeable intracellular Ca2+ chelator that can be loaded non-invasive into cells by incubation. MAPTAM itself does not bind calcium, but once inside the cell is converted into its derivative Dimethyl-BAPTA by cytoplasmic esterases. This type of calcium chelators are commonly used to form calcium buffers with well-defined calcium concentrations. By injecting the chelators into cells or by incubating cells with the AM ester form of the chelators, one can control the cytosolic calcium concentration, an important means to study the roles of calcium. Key advantages of these calcium chelators include relative insensitivity toward intracellular pH change and fast release of calcium. Recent studies have shown that BAPTA derivative might have microtubule disruptive activity (unrelated to its calcium chelating activity) and should be used with caution in studies of cytoskeleton-related cell functions. - MAPTAM is a cell permeable intracellular Ca2+ chelator that can be loaded non-invasive into cells by incubation. MAPTAM itself does not bind calcium, but once inside the cell is converted into its derivative Dimethyl-BAPTA by cytoplasmic esterases. This type of calcium chelators are commonly used to form calcium buffers with well-defined calcium concentrations. By injecting the chelators into cells or by incubating cells with the AM ester form of the chelators, one can control the cytosolic calcium concentration, an important means to study the roles of calcium. Key advantages of these calcium chelators include relative insensitivity toward intracellular pH change and fast release of calcium. Recent studies have shown that BAPTA derivative might have microtubule disruptive activity (unrelated to its calcium chelating activity) and should be used with caution in studies of cytoskeleton-related cell functions.
- SMILESCC1=CC(OCCOC2=CC(C)=CC=C2N(CC(OCOC(C)=O)=O)CC(OCOC(C)=O)=O)=C(N(CC(OCOC(C)=O)=O)CC(OCOC(C)=O)=O)C=C1
- Storage Instruction2°C to 8°C,-20°C
- UNSPSC12352200
