Functional antibodies
Potent blocking, neutralizing, activating antibodies (including non-animal source antibodies) for in vivo studies.
Key inflammasome research tools from AdipoGen Life Sciences
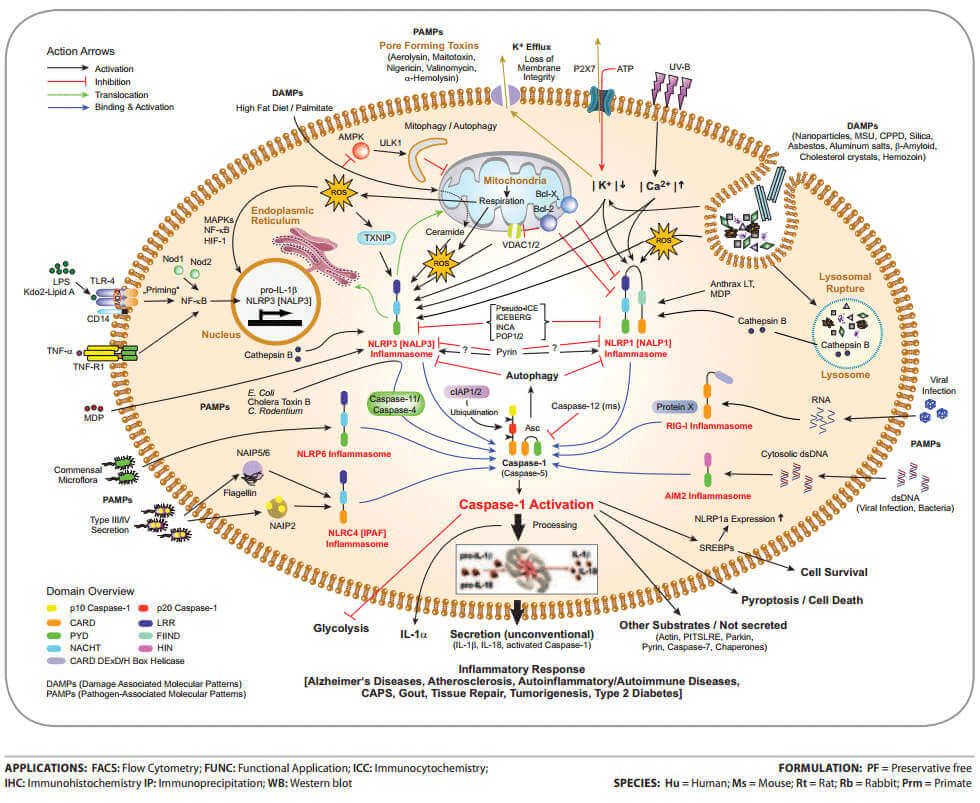
Inflammasomes are multi-protein complexes whose activity has been implicated in physiological and pathological inflammation. The hallmarks of inflammasome activation are the secretion of the mature forms of caspase-1 and interleukin-1β (IL-1β) from cells of the innate immune system.
An inflammasome represents a high molecular weight complex that activates inflammatory caspases and cytokines of the IL-1 family (IL-1β, IL-18 and depending on the stimulus also IL-1α). Several inflammasomes have been described which contain different sensor proteins such as NLRP1 (NALP1), NLRP3 (NALP3), IPAF (NLRC4), NLRP6 (NALP6), RIG-I and AIM-2 (absent in melanoma 2). Most of these inflammasomes require the adapter protein Asc (apoptosis-associated specklike protein containing a caspase recruitment domain) to recruit caspase-1 to the inflammasome complex. Upon binding to the inflammasome caspase-1 is cleaved and activated, leading to cleavage of its various targets and causing maturation and secretion of the pro-inflammatory IL-1β. Inflammasomes can be activated through multiple signals including live bacteria, microbial toxins, xeno-compounds, cytoplasmic pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) and/or endogenous danger signals (DAMPs).
Inflammasome activity has been causally linked to the induction of numerous inflammatory responses, which can be either beneficial or harmful to the organism. Beneficial responses arise by maintaining homeostatic tissue function (detection and repair of tissue damages after trauma or pathogen invasion). Among the harmful inflammatory responses are particle-induced sterile inflammation, caused by host-derived particles such as monosodium urate (MSU) crystals, which are involved in the pathogenesis of gout, as well as environmental and industrial particles such as asbestos, silica and metallic nanoparticles, which include lung inflammation upon inhalation. Accumulating evidence also implicates inflammasome activity in numerous other diseases, including cancer and the development of metabolic diseases like type 2 diabetes, atherosclerosis and inflammatory bowel diseases. Beneficial effects for the host include the enhancement of vaccine efficacy.
Priming of the NLRP3 inflammasome
The most prominent function of the NLRP3 inflammasome is the processing and activation of pro-interleukin-1β (pro-IL-1β). Yet most cells do not express pro-IL-1β and thus prior expression of pro-IL-1β is required. This can be achieved by stimulating receptors such as TLRs (e.g. LPS), NODs or TNF-Rs (e.g. TNF-α) that activate NF-κB and initiate pro-IL-1β transcription. This process of pro-IL-1β induction is called priming (Signal 1). Priming also induces NF-κB-dependent transcription of NLRP3. An additional stimulus (Signal 2) results in the activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome and subsequent initiation of downstream signaling. In the absence of priming, NLRP3 inflammasome-dependent caspase-1 activation can also be observed, but IL-1β secretion is absent.
| TNF-alpha, Soluble (human) (rec.) (AG-40B-0006-C010) |
| TNF-alpha (human) (multimeric) (rec.) (AG-40B-0019-C010) |
| TNF-alpha (mouse) (multimeric) (rec.) (AG-40B-0021-C010) |
| Lipopolysaccharides (LPS) (IAX-100) |
Inflammasomes are large multimolecular complexes involved in innate immune response and driving cell fate towards cell death, called pyroptosis. Stress granules are aggregates formed during cellular stress with pro-survival role composed of proteins and mRNA molecules. Recently, the lab of Prof. Thirumala-Devi Kanneganti (St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital, Memphis) describes a new role of the stress granules in inhibiting the inflammasome. The stress granule protein DDX3X interacts with NLRP3 to activate the inflammasome. Assembly of stress granules leads to the sequestration of DDX3X, and thereby the inhibition of NLRP3 inflammasome activation. With this dual function, DDX3X regulates a live-or-die cell-fate decisions under stress conditions.
| anti-Caspase-1 (p20) (mouse), mAb (Casper-1) (AG-20B-0042-C100) |
| anti-NLRP3/NALP3, mAb (Cryo-2) (AG-20B-0014-C100) |
| anti-Asc, pAb (AL177) (AG-25B-0006-C100) |
We gladly support you by keeping you updated on our latest products and the developments around our services.