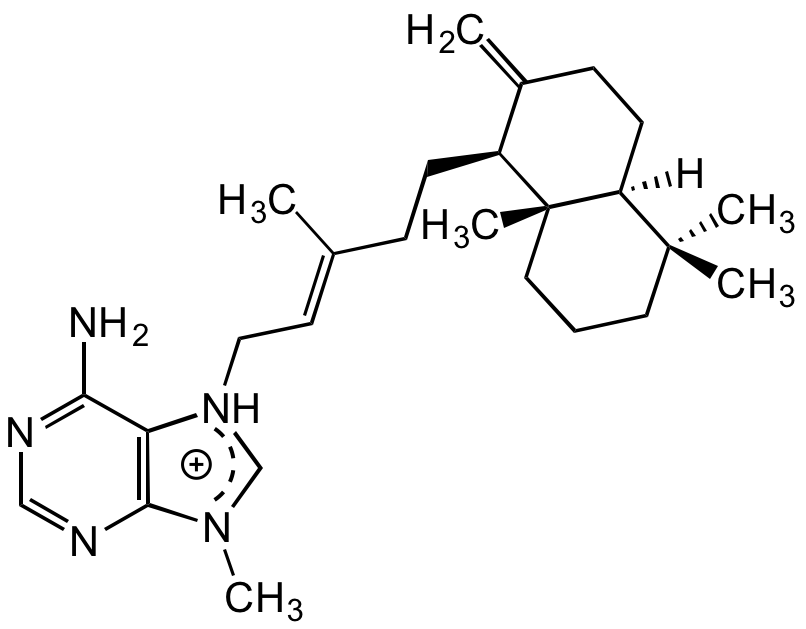
Chemical Structure
Agelasine D [92664-80-7]

AG-CN2-0492
CAS Number92664-80-7
Product group Chemicals
Estimated Purity>97% (HPLC)
Molecular Weight422.6
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product NameAgelasine D [92664-80-7]
- Delivery Days Customer10
- CAS Number92664-80-7
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>97% (HPLC)
- Hazard InformationNon-hazardous
- Molecular FormulaC26H40N5
- Molecular Weight422.6
- Scientific DescriptionAntifouling compound. Antimycobacterial and antibacterial agent. Exerts its antibacterial effect by inhibiting enzyme BCG 3185c, a suspected dioxygenase thereby disrupting bacterial homeostasis. Associated with contractive responses of smooth muscles and inhibition of Na+/K+ ATPase. Cytotoxic/Antineoplastic agent. Found to exhibit inhibitory activity against several cancer cell lines, including the drug resistant renal cancer cell line (ACHN). Suppressor of RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis via down-regulation of c-Fos, NFATc1, NF-kappaB and ERK. Antiprotozoal compound. - Chemical. CAS: 92664-80-7. Formula: C26H40N5. MW: 422.6. Isolated from sponge Agelas sp. Antifouling compound. Antimycobacterial and antibacterial agent. Exerts its antibacterial effect by inhibiting enzyme BCG 3185c, a suspected dioxygenase thereby disrupting bacterial homeostasis. Associated with contractive responses of smooth muscles and inhibition of Na+/K+ ATPase. Cytotoxic/Antineoplastic agent. Found to exhibit inhibitory activity against several cancer cell lines, including the drug resistant renal cancer cell line (ACHN). Suppressor of RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis via down-regulation of c-Fos, NFATc1, NF-kappaB and ERK. Antiprotozoal compound.
- SMILESC/C(CC[C@H]1C(CC[C@]2([H])[C@]1(C)CCCC2(C)C)=C)=C\C[NH]3CN(C)C4=C3C(N)=NC=N4
- Storage Instruction2°C to 8°C,-20°C
- UNSPSC12352200
References
- Agelasine-A -B, -C and -D, novel bicyclic diterpenoids with a 9-methyladeninium unit possessing inhibitory effects on Na,K-ATPase isolated from the Okinawian sea sponge Agelas sp: H. Nakamura, et al.; Tetrahedron Lett. 25, 2989 (1984)
- (+)-agelasine D: improved synthesis and evaluation of antibacterial and cytotoxic activities: A. Vik, et al.; J. Nat. Prod. 69, 381 (2006)
- Synthesis, antimicrobial and antineoplastic activities for agelasine and agelasimine analogs with a beta-cyclocitral derived substituent: A. Proszenyak, et al.; Arch. Pharm. 340, 625 (2007)
- Antifouling activity of the sponge metabolite agelasine D and synthesised analogs on Balanus improvisus: M. Sjoegren, et al.; Biofouling 24, 251 (2008)
- Screening of Agelasine D and Analogs for Inhibitory Activity against Pathogenic Protozoa; Identification of Hits for Visceral Leishmaniasis and Chagas Disease: A. Vik, et al.; Molecules 14, 279 (2009)
- From anti-fouling to biofilm inhibition: New cytotoxic secondary metabolites from two Indonesian Agelas sponges: T. Hertiani, et al.; Bioorg. Med. Chem. 18, 1297 (2010)
- Synthesis and biological activities of marine terpene-adenine hybrids and synthetic analogs: L.-L. Gundersen; Phytochem. Rev. 12, 467 (2013) (Review)
- Identification of the target protein of agelasine D, a marine sponge diterpene alkaloid, as an anti-dormant mycobacterial substance: M. Arai, et al.; Chembiochem. 15, 117 (2014)
- Agelasine D suppresses RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis via down-regulation of c-Fos, NFATc1 and NF-kappaB: M.R. Kang, et al.; Mar. Drugs 12, 5643 (2014)
