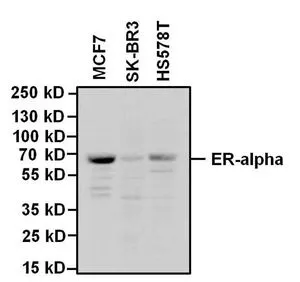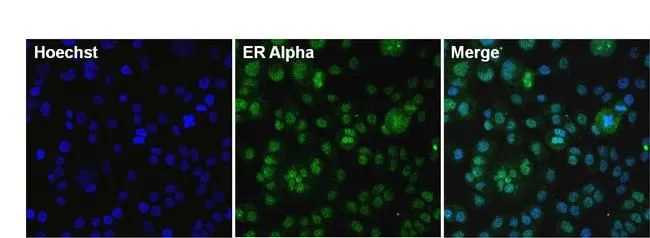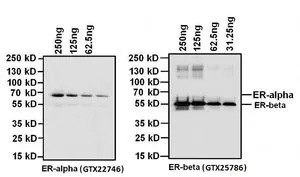
GTX22746 WB Image
Estrogen Receptor alpha antibody [33]

GTX22746
ApplicationsGel Shift Assay, Flow Cytometry, ImmunoFluorescence, ImmunoPrecipitation, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityAvian, Bovine, Fish, Human, Mouse, Primate, Rat
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameEstrogen Receptor alpha antibody [33]
- Delivery Days Customer10
- ApplicationsGel Shift Assay, Flow Cytometry, ImmunoFluorescence, ImmunoPrecipitation, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone ID33
- Concentration1 mg/ml
- HostMouse
- IsotypeIgG
- Scientific DescriptionThis gene encodes an estrogen receptor, a ligand-activated transcription factor composed of several domains important for hormone binding, DNA binding, and activation of transcription. The protein localizes to the nucleus where it may form a homodimer or a heterodimer with estrogen receptor 2. Estrogen and its receptors are essential for sexual development and reproductive function, but also play a role in other tissues such as bone. Estrogen receptors are also involved in pathological processes including breast cancer, endometrial cancer, and osteoporosis. Alternative promoter usage and alternative splicing result in dozens of transcript variants, but the full-length nature of many of these variants has not been determined. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2014]
- ReactivityAvian, Bovine, Fish, Human, Mouse, Primate, Rat
- Storage Instruction2°C to 8°C,-20°C
- UNSPSC12352203
References
- Estrogen receptors orchestrate cell growth and differentiation to facilitate liver regeneration. Kao TL et al., 2018, TheranosticsRead more
- Functional interaction of DYX1C1 with estrogen receptors suggests involvement of hormonal pathways in dyslexia. Massinen S et al., 2009 Aug 1, Hum Mol GenetRead more