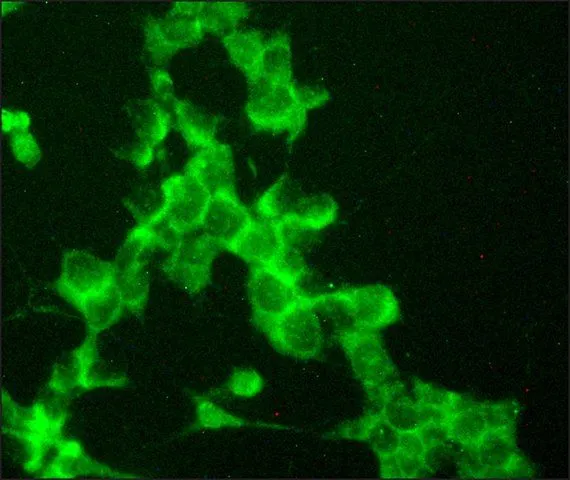
GTX10494 ICC/IF Image
p75 NGF Receptor / CD271 antibody

GTX10494
ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Frozen
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityRat
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product Namep75 NGF Receptor / CD271 antibody
- Delivery Days Customer10
- ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Frozen
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
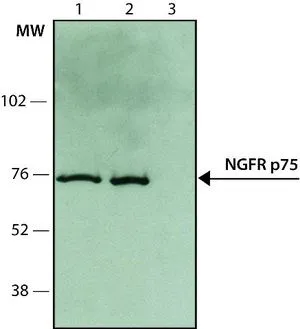
- Scientific DescriptionNerve Growth Factor Receptor, also termed NGFR p75 or p75NTR, is the low-affinity NGFR (LNGFR) which binds NGF and other neurotrophins including BDNF, NT3, NT4/5 with similar, low affinity. NGFR p75 is a 75kD transmembrane glycoprotein (399 a.a.) consisting of an extracellular domain (222 a.a.) which contains four cysteine-rich domains responsible for ligand binding, a transmembrane domain (22 a.a.), and a cytoplasmic domain (155 a.a.). NGFR p75 is mainly expressed in Schwann cells and neurons and in a variety of non-neuronal cells. NGFR p75 is necessary for regulating neuronal growth, migration, differentiation and cell death during development of the central and peripheral nervous system. The signal transduction mechanisms and components leading to NGFR p75 multiple signals are complex and not well understood. In contrast to other members of the neurotrophin receptors family (TrkA, TrkB and TrkC tyrosine kinases), NGFR p75 lacks intrinsic catalytic activity. It has been suggested that NGFR p75 interacts with TrkA to form high affinity binding sites and to modulate TrkA signaling. NGFR p75 belongs to the TNF receptor superfamily which includes TNFR, CD40 and Fas. These receptors all have an intracellular death domain and can couple to parallel signaling pathways leading to apoptotic cell death or activation of the transcription factor NF-kappaB. NGFR p75 plays a central role in the regulation of cell number by apoptosis in the developing CNS. During early development, activation of NGFR p75 by NGF induces apoptotic cell death in some neuronal cells, probably through activation of the sphingomyelinase/ceramide pathway, the ICE-like proteases and the JNK pathway. In rat Schwann cells, NGF binding to NGFR p75 activates NF-kappaB, possibly to modulate Schwann cell migration during nerve regeneration.
- ReactivityRat
- Storage Instruction2°C to 8°C,-20°C
- UNSPSC12352203