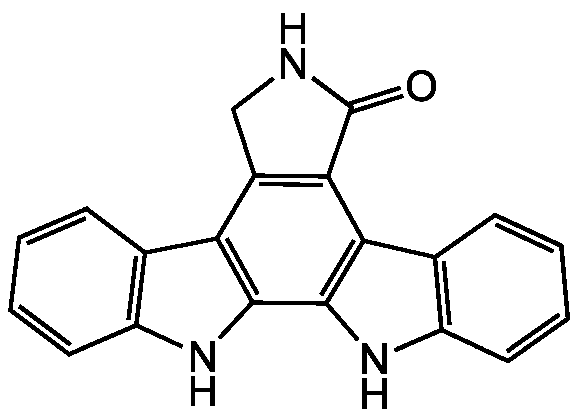
Chemical Structure
K-252c [85753-43-1]

AG-CN2-0097
CAS Number85753-43-1
Product group Chemicals
Estimated Purity>97% (HPLC)
Molecular Weight311.4
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product NameK-252c [85753-43-1]
- Delivery Days Customer10
- CAS Number85753-43-1
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>97% (HPLC)
- Hazard InformationNon-hazardous
- Molecular FormulaC20H13N3O
- Molecular Weight311.4
- Scientific DescriptionChemical. CAS: 85753-43-1. Formula: C20H13N3O. MW: 311.4. Isolated from Streptomyces longisporoflavus. Indolocarbazole alkaloid antibiotic. Potent cell permeable reversible and ATP-competitive PKC (protein kinase C) inhibitor with 10-fold selectivity over PKA (protein kinase A). Anticancer compound. Cytotoxic againt various cancer cell lines. Apoptosis inducer. Antiviral compound against GCV-sensitive and -resistant strains of human cytomegalovirus (HCMV). LACTB (beta-lactamase), malate dehydrogenase (MDH2, MDHC, MDH1B, ME1. ME2, ME3) and chymotrypsin inhibitor. Inhibits mixed lineage kinase (MLK). - Indolocarbazole alkaloid antibiotic. [1]. Potent cell permeable reversible and ATP-competitive PKC (protein kinase C) inhibitor with 10-fold selectivity over PKA (protein kinase A) [1-5]. Anticancer compound. Cytotoxic againt various cancer cell lines [6, 9,11]. Apoptosis inducer [11]. Antiviral compound against GCV-sensitive and -resistant strains of human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) [7]. LACTB (beta-lactamase), malate dehydrogenase (MDH2, MDHC, MDH1B, ME1. ME2, ME3) and chymotrypsin inhibitor [8]. Inhibits mixed lineage kinase (MLK) [10].
- SMILESO=C1NCC2=C1C1=C(NC3=C1C=CC=C3)C1=C2C2=C(N1)C=CC=C2
- Storage Instruction2°C to 8°C,-20°C
- UNSPSC12352200
References
- K-252b, c and d, potent inhibitors of protein kinase C from microbial origin: S. Nakanishi, et al.; J. Antibiot. 39, 1066 (1986)
- The structures of the novel protein kinase C inhibitors K-252a, b, c and d: T. Yasuzawa, et al.; J. Antibiot. 39, 1072 (1986)
- Staurosporine, K-252 and UCN-01: potent but nonspecific inhibitors of protein kinases: U.T. Ruegg & G.M. Burgess; TIPS 10, 218 (1989)
- Protein kinase C inhibitors; structure-activity relationships in K252c-related compounds: S. Fabre, et al.; Bioorg. Med. Chem. 1, 193 (1993)
- Non-glycosidic/non-aminoalkyl-substituted indolocarbazoles as inhibitors of protein kinase C: J. Kleinschroth, et al.; Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 3, 1959 (1993)
- Staurosporine aglycone (K252-c) and arcyriaflavin A from the marine ascidian, Eudistoma sp: P.A. Horton, et al.; Experientia 50, 843 (1994)
- Indolocarbazoles exhibit strong antiviral activity against human cytomegalovirus and are potent inhibitors of the pUL97 protein kinase: A. Zimmermann, et al.; Antiviral Res. 48, 49 (2000)
- Kinase inhibitors: not just for kinases anymore: S.L. McGovern & B.K. Shoichet; J. Med. Chem. 46, 1478 (2003)
- Biological targets of antitumor indolocarbazoles bearing a sugar moiety: M. Prudhomme; Curr. Med. Chem. Anticancer Agents 4, 509 (2004)
- Synthesis and mixed lineage kinase activity of pyrrolocarbazole and isoindolone analogs of (+)K-252a: R.L. Hudkins, et al.; J. Med. Chem. 50, 433 (2007)
