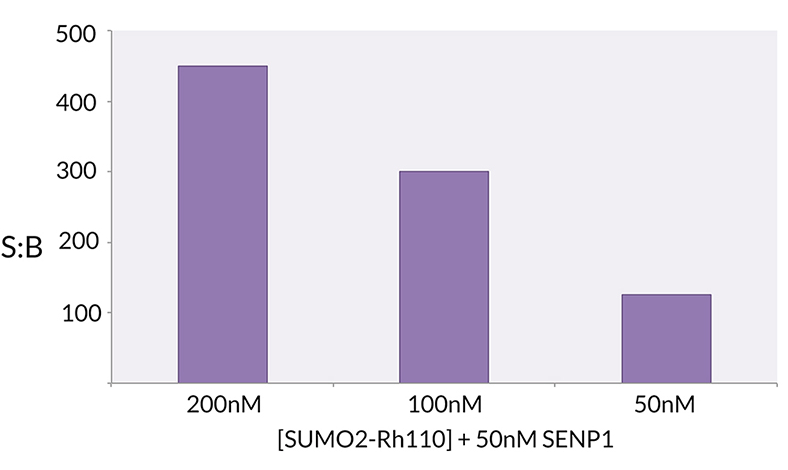
Signal to Background: The signal to background ratio was determined by 100% hydrolysis of 200nM, 100nM, 50nM SUMO2-Rhodamine 110 to liberate the quenched conjugate. Assay Buffer: 50mM HEPES pH 7.5, 1mM TCEP, 0.1mg/ml BSA.
SUMO2 (human) (rec.) (Rhodamine 110)

SBB-PS0029
Overview
- SupplierSouth Bay Bio
- Product NameSUMO2 (human) (rec.) (Rhodamine 110)
- Delivery Days Customer10
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>97%
- Protein IDP61956
- Protein NameSmall ubiquitin-related modifier 2
- Scientific DescriptionProtein. Human SUMO2 (aa1-93)conjugated at the C-terminus to a quenched Rhodamine 110 dye. Source: E. coli. Formulation: Liquid. In 50mM HEPES pH 7.5, 100mM sodium chloride. Purity: >97% (LCMS). SUMO2 is a Ubiquitin-like protein (UBL) that can be covalently attached to proteins as a monomer or as a lysine-linked polymer. Covalent attachment via an isopeptide bond to its substrates requires prior activation by the E1 complex SAE1-SAE2 and linkage to the E2 enzyme UBE2I, and can be promoted by an E3 ligase such as PIAS1-4, RANBP2, CBX4 or ZNF451. This post-translational modification on lysine residues of proteins plays a crucial role in a number of cellular processes such as nuclear transport, DNA replication and repair, mitosis and signal transduction. This SUMO2 substrate is C-terminally derivatized with a bis-Gly-Rhodamine 110 fluorophore. The bis-Gly-Rh110 is quenched until the amide bond between the C-terminal glycine and the rhodamine compound is hydrolyzed. The efficiency of quenching combined with the powerful signal upon hydrolysis yields an unparalleled signal-to-background. SUMO2-Rh110 can be used to study the deSUMOylating activity of hydrolases SENP1 and SENP2, among other deSUMOylating enzymes. The substrate activity of SUMO2-Rhodamine 110 was determined by measuring the SENP1 catalyzed release of unquenched Gly-Rh-110. - SUMO2 is a Ubiquitin-like protein (UBL) that can be covalently attached to proteins as a monomer or as a lysine-linked polymer. Covalent attachment via an isopeptide bond to its substrates requires prior activation by the E1 complex SAE1-SAE2 and linkage to the E2 enzyme UBE2I, and can be promoted by an E3 ligase such as PIAS1-4, RANBP2, CBX4 or ZNF451. This post-translational modification on lysine residues of proteins plays a crucial role in a number of cellular processes such as nuclear transport, DNA replication and repair, mitosis and signal transduction. This SUMO2 substrate is C-terminally derivatized with a bis-Gly-Rhodamine 110 fluorophore. The bis-Gly-Rh110 is quenched until the amide bond between the C-terminal glycine and the rhodamine compound is hydrolyzed. The efficiency of quenching combined with the powerful signal upon hydrolysis yields an unparalleled signal-to-background. SUMO2-Rh110 can be used to study the deSUMOylating activity of hydrolases SENP1 and SENP2, among other deSUMOylating enzymes. The substrate activity of SUMO2-Rhodamine 110 was determined by measuring the SENP1 catalyzed release of unquenched Gly-Rh-110.
- Storage Instruction-80°C
- UNSPSC12352202
