Functional antibodies
Potent blocking, neutralizing, activating antibodies (including non-animal source antibodies) for in vivo studies.
Clinically relevant antibodies in various Ig isotypes
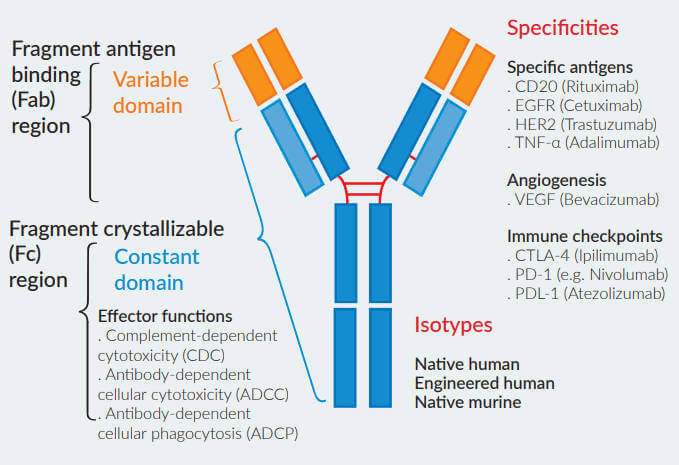
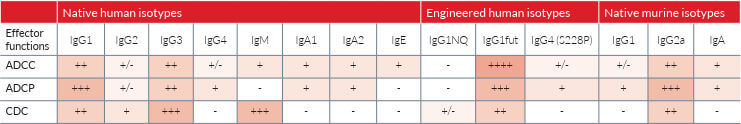
InvivoGen provides a series of clinically relevant antibodies in their original format or with different immunoglobulin isotypes. Their engineered antibodies are designed to adjust their effector functions, including half-life, complementdependent cytotoxicity (CDC), antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) and antibody-dependent cell phagocytosis (ADCP). The variety of the immunoglobulin constant regions helps you determine the most suitable isotype for your application.
Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) have become a major tool in the treatment of cancer and auto-immune diseases. The efficacy of antibodies is governed by their bifunctional nature. On the one hand, the variable domain of the immunoglobulin, within the fragment of antigen binding (Fab), confers antigen specificity function. On the other hand, the fragment crystallizable region (Fc) in the constant domain of the immunoglobulin triggers antibody-mediated effector functions by engaging a variety of Fc receptors. Antibody isotype switching is a biological process enabling changes in the ability of the antibody to interact with different Fc receptors and thus, reduce or potentiate effector functions. InvivoGen’s antibody isotype families consist of clinically relevant mAbs comprising the same variable domain and the constant domain of various isotypes, therefore differing in their suitability for a given application.
| Product | Isotype |
|---|---|
| Anti-hCD20-hIgG1 | Human IgG1 |
| Anti-hCD20-hIgG1NQ | Human IgG1, non-glycosylated |
| Anti-hCD20-hIgG1fut | Human IgG1, non-fucosylated |
| Anti-hCD20-hIgG2 | Human IgG2 |
| Anti-hCD20-hIgG3 | Human IgG3 |
| Anti-hCD20-hIgG4 (S228P) | Human IgG4 (S228P) |
| Anti-hCD20-hIgA2 | Human IgA2 |
| Anti-hCTLA4-hIgG1 | Human IgG1 |
| Anti-hCTLA4-hIgG1fut | Human IgG1, non-fucosylated |
| Anti-hCTLA4-hIgG4 (S228P) | Human IgG4 (S228P) |
| Anti-hEGFR-hIgG1 | Human IgG1 |
| Anti-HER2-Tra-hIgG1 | Human IgG1 |
| Anti-HER2-Tra-hIgG4 (S228P) | Human IgG4 (S228P) |
| Anti-HER2-Tra-hIgA2 | Human IgA2 |
| Anti-hPD1-Ni-hIgG1 | Human IgG1 |
| Anti-hPD1-Ni-hIgG4 (S228P) | Human IgG4 (S228P) |
| Anti-hPD1-Pem-hIgG1 | Human IgG1 |
| Anti-hPD1-Pem-hIgG4 (S228P) | Human IgG4 (S228P) |
| Anti-hPD-L1-hIgG1 | Human IgG1 |
| Anti-hPD-L1-hIgG1 (N298A) | Human IgG1, (N298A) |
| Anti-hPD-L1-hIgG1fut | Human IgG1, non-fucosylated |
| Anti-TNF-alpha-hIgG1 | Human IgG1 |
| Anti-TNF-alpha-hIgG4 | Human IgG4 |
| Anti-TNF-alpha-hIgA2 | Human IgA2 |
We gladly support you by keeping you updated on our latest products and the developments around our services.