MCE Bioactive Compound Libraries
MedChem Express (MCE) One-Stop Compound Screening Platform supplies more than 200 screening libraries and a variety of compounds and phenotypic screening service.
MCE provides a wide range of immune checkpoint eukaryotic recombinant proteins, offering high-quality raw materials and tools for immune checkpoint research.
Immune checkpoint (IC) proteins are key molecules that regulate the immune system by maintaining immune tolerance, determining the timing of the immune response, and controlling the intensity of the immune stress. Tumor cells exploit the immune checkpoint pathway as a major mechanism for immune escape, particularly by evading responses from immune cells that are capable of recognizing tumor-specific antigens presented by T cells[1]. Therefore, agonists of co-stimulatory signaling or antagonists of inhibitory signaling represent promising approaches for cancer treatment. Classical immune checkpoint proteins include co-inhibitory receptors that inhibit T cell function (CTLA-4, PD-1, TIGIT, LAG-3) and co-stimulatory receptors that stimulate T cell function (GITR, 4-1BB, OX40, CD40).
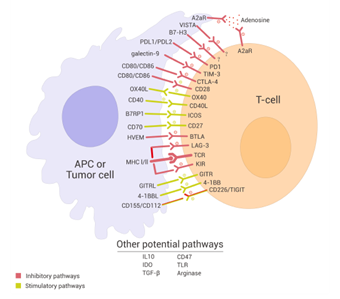
PD-1 and CTLA-4 are the most well-known negative regulatory receptors in the immune system, both of which counteract T-cell receptor-mediated immune activation[3].
Programmed cell death 1 (PD-1), a member of the CD28 superfamily, is a type I transmembrane protein consisting of 268 amino acids[4]. Expressed on the surface of T cells, PD-1 binds to programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) on tumor cells and programmed death-ligand 2 (PD-L2) on antigen-presenting cells. This interaction induces apoptosis of T lymphocytes, impairs the body’s anti-tumor immune response, and ultimately leads to the immune escape of tumor cells.
Cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated antigen 4 (CTLA4) is expressed on the surface of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells and binds to CD80/CD86 on antigen-presenting cells, generating signals that inhibit T-cell activation and reduce the body’s anti-tumor immune response[5]. CTLA-4 monoclonal antibodies can attenuate the inhibitory effect of CTLA-4 on T cells, thereby enhancing the anti-tumor effect of the body’s immune cells.
MCE provides a wide range of immune checkpoint eukaryotic recombinant proteins, offering high-quality raw materials and tools for immune checkpoint research. Below is a list of targets:
| Target Name | Specices | Source | Tag | Cat No |
| PD-L1 | Mouse | Mammalian cells | C-6*His | HY-P70691 |
| PD-1 | Human | Mammalian cells | C-hFc | HY-P7395 |
| CTLA-4 | Human | Mammalian cells | C-GST | HY-P70691 |
| TIM3 | Human | Mammalian cells | C-6*His | HY-P70482 |
| LAG-3 | Human | Mammalian cells | C-6*His | HY-P70722 |
| TIGIT | Human | Mammalian cells | C-6*His | HY-P70624 |
| B7-H3 | Human | Mammalian cells | C-6*His | HY-P7327 |
We gladly support you by keeping you updated on our latest products and the developments around our services.