Cygnus Custom Development Services
Benefit from Cygnus’ knowledge in developing immunochemical reagents and methods for bioproduction impurities
Now, using Cygnus’s BSL-1 compatible viral clearance kits, you can easily and economically quantify viral clearance for downstream process steps right in your own lab and on your timeline.
Viral contamination is an inherent risk during the manufacture of biopharmaceutical products. Whether introduced initially from raw materials or later through specific manufacturing operations, unmitigated viral contamination has led to serious health implications and plant shutdowns. Global regulatory agencies require sponsoring companies to validate the viral clearance efficacy of their purification process steps prior to clinical trials or regulatory approval. Currently, this is accomplished with live virus “spiking” studies whereby model viruses are artificially introduced into biopharmaceutical material and subsequently removed via downstream manufacturing purification steps. Spiking studies require specialized contract research organizations (CROs) and trained personnel resulting in high costs and complex logistics. These hurdles deter companies from analyzing viral clearance during the years of small-scale process development. Instead, companies spend considerable resources optimizing manufacturing processes before gaining any knowledge of their viral clearance efficacy. Unfortunately, this increases the risk of validation failure, forcing companies to invest additional time and money redeveloping process steps, which in turn, could postpone regulatory approvals and delay patients’ timely access to therapies.
Cygnus’ MockV® technology address the barriers imposed by live viral clearance studies through the novel and patent protected use of viral surrogates, or “Mock Viral Particles (MVPs)”. MVPs are engineered to mimic the physical and chemical characteristics of viruses but are themselves non-infectious. They can therefore be handled safely and easily to predict the outcomes of CRO-led spiking studies.
Why delay until late phase clinical manufacturing before testing if your downstream purification process steps provide sufficient viral clearance? Instead, you can now gain actionable insights early in process development. The Cygnus MockV® RVLP Kit provides a BSL-1 compatible stock solution of non-infectious Retrovirus-like Particles (RVLP), derived endogenously from CHO cell culture, as a spiking agent for viral clearance testing. The kit enables prediction of retroviral validation outcomes and allows incorporation of viral clearance to QbD, DOE and HTS approaches. Instead of relying solely on a CRO-provided model retrovirus (XMuLV), process development groups can now independently spike and assess the removal of the original retrovirus particle of regulatory concern1.
Non-infectious RVLP were produced during CHO cell cultivation and purified via multiple modes of chromatography before being concentrated to a final stock solution of 1 x 1010 particles/mL (Figure 1).
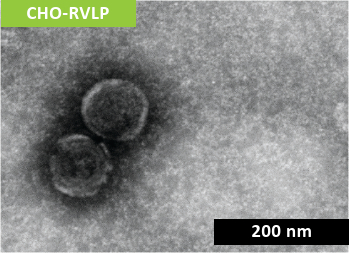
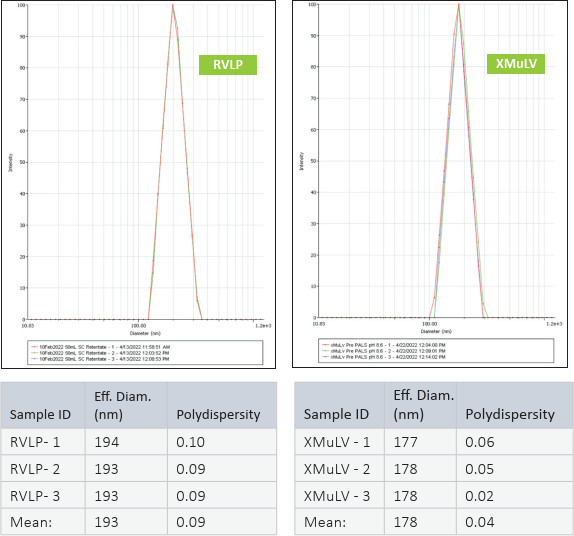
RVLP diameter and net-surface charge were assessed alongside XMuLV (produced by Texcell, N.A.) via Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS) and Zeta Potential. The DLS results demonstrated that RVLP, are monodisperse and exhibit an average diameter of 193 nm while XMuLV are also monodisperse but exhibit a slightly smaller diameter.
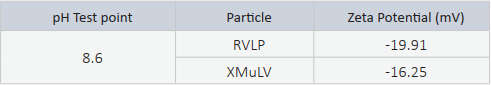
Zeta Potential results indicated that the surface charge of each particle were slightly acidic.
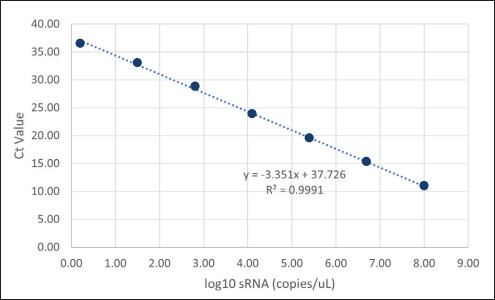
To analyze the concentration of noninfectious RVLP in samples, an RT-qPCR method modified from De Wit, 2000 was employed. In short, samples were added to a 96 deep-well plate and were treated with Endonuclease to degrade CHO-endogenous RVLP DNA sequences. RNA was then extracted from RVLP and precipitated with a set of proprietary buffers (Cygnus Technologies, LLC). The plate was then stored at -20 °C for 30 minutes and RNA was pelleted via centrifugation at 3,000 × g for 20 minutes at 4 °C. After washing and final pelleting, the RNA was resuspended in a proprietary buffer. 10 μL of sample was transferred from each well of the 96 deep-well plate to a qPCR plate containing TaqMan primers/probe directed against the pol region of the CHO-RVLP genome. To determine the quantity of particles in unknown samples, threshold cycle (Ct) values were interpolated into a standard curve generated by including a dilution series of a known sRNA standard. From those concentration values, RVLP LRVs for each experiment were calculated.
The MockV® RVLP Kit (M230) includes a vial of RVLP stock solution, a 96-well plate for sample analysis, RNA extraction and qPCR reagents, and a well-controlled RNA standard for accurate and reliable RVLP quantification. By following the kit’s easy-to-use protocol, scientists can detect as little as 1 × 103 RVLP/mL, enabling LRV of ~ 5.0 to be determined. Each kit contains 2.0 mL of RVLP Stock Solution at a concentration of 1 × 1010 RVLP/mL sufficient for spiking up to 200 mL of load material to 1% (v/v) and conducting analysis on 23 samples in triplicate in less than one day. A real-time qPCR instrument is required along with standard laboratory equipment. Minimal experience with RNA extraction or qPCR protocols is required. Compatible purification steps include Protein A chromatography, virus filtration, anion and cation exchange chromatography, mixed-mode, hydrophic-interaction and size- exclusion chromatography. MockV RVLP Kit achieves LRV accuracy to within ± 0.5 for these modes of separation as compared to traditional viral clearance studies with XMuLV model virus.
Now, using Cygnus’s BSL-1 compatible viral clearance kits, you can easily and economically quantify viral clearance for downstream process steps right in your own lab and on your timeline.
QbD = Quality by Design
DOE = Design of Experiment
HTS = High-throughput Screening
To learn more about Cygnus MockV® RVLP and MockV® MVM Kits, visit: Mockv.info
We gladly support you by keeping you updated on our latest products and the developments around our services.